犬猫の眼球内圧計測に対するPerkinハンディ圧平眼圧計の評価
Evaluation of the Perkins handheld applanation tonometer in the measurement of intraocular pressure in dogs and cats.
犬猫の眼圧計測におけるPerkinハンディ圧平眼圧計の評価
Andrade SF, Cremonezi T, Zachi CAM, et al. Evaluation of the Perkins handheld applanation tonometer in the measurement of intraocular pressure in dogs and cats. Vet Ophthalmol. 2009;12(5):277-284. doi:10.1111/j.1463-5224.2009.00702.x / PMID: 19751486
論文アブストラクト(PubMed)はこちら
[su_service title=”論文アブストラクト” icon=”icon: book” size=”18″][/su_service]
[su_tabs][su_tab title=”原文” disabled=”no” anchor=”” url=”” target=”blank” class=””]
OBJECTIVE:
To evaluate and to validate the accuracy of the Perkins handheld applanation tonometer in the measurement of IOP in dogs and cats.
ANIMALS:
Twenty eyes from 10 dogs and 10 cats immediately after sacrifice were used for the postmortem study and 20 eyes from 10 clinically normal and anesthetized dogs and cats were used for the in vivo study. Both eyes of 20 conscious dogs and cats were also evaluated.
PROCEDURE:
Readings of IOP postmortem and in vivo were taken using manometry (measured with a mercury column manometer) and tonometry (measured with a Perkins handheld applanation tonometer). The IOP measurement with Perkins tonometer in anesthetized and conscious dogs and cats was accomplished by instillation of proxymetacaine 0.5% and of 1% fluorescein eye drops.
RESULTS:
The correlation coefficient (r(2)) between the manometry and the Perkins tonometer were 0.982 (dogs) and 0.988 (cats), and the corresponding linear regression equation were y = 0.0893x + 0.1105 (dogs) and y = 0.0899x + 0.1145 (cats) in the postmortem study. The mean IOP readings with the Perkins tonometer after calibration curve correction were 14.9 +/- 1.6 mmHg (range 12.2-17.2 mmHg) in conscious dogs, and were 15.1 +/- 1.7 mmHg (range 12.1-18.7 mmHg) in conscious cats.
CONCLUSION:
There was an excellent correlation between the IOP values obtained from direct ocular manometry and the Perkinstonometer in dogs and cats. The Perkins handheld tonometer could be in the future a new alternative for the diagnosis of glaucoma in veterinary ophthalmology.
[/su_tab] [su_tab title=”自動翻訳” disabled=”no” anchor=”” url=”” target=”blank” class=””]
目的:
Perkin手持ち圧平式眼圧計について、犬猫のIOP測定に対する正確さを評価・確認するため。
動物:
10頭のイヌおよび10頭のネコの安楽死直後の20眼球を用いて死後剖検研究を行い、麻酔された10頭の臨床的に正常なイヌおよびネコの20眼球をin vivo研究に用いた。20頭の覚醒したイヌおよびネコの両眼も評価した。
手技:
剖検時およびin vivoでのIOPは、圧力計を用いて(マノメトリーを用いて計測)および眼圧計を用いて(Perkin手持ち式圧平眼圧計を用いて計測)測定した。麻酔下および覚醒状態の犬猫での、Perkin眼圧計を用いたIOPは、0.5%プロキシメタカインおよび1%フルオレセイン点眼液を滴下することにより得られた。
結果:
剖検研究では、圧力計とPerkin眼圧計との相関係数(r(2))は0.982(イヌ)および0.988(ネコ)であり、対応する直線回帰式はy = 0.0893x + 0.1105(イヌ)および y = 0.0899x + 0.1145(ネコ)であった。キャリブレーションカーブ補正後のPerkin眼圧計を用いた場合の平均IOPは、覚醒犬で14.9 +/- 1.6 mmHg(12.2-17.2 mmHgの範囲)、覚醒猫で15.1 +/- 1.7 mmHg(12.1-18.7 mmHgの範囲)であった。
まとめ:
犬猫では、直接測定して得られた眼球圧力とPerkinの眼圧計で得られた値との間には強い相関が存在した。Perkinのハンディタイプの眼圧計は将来的に、獣医眼科学で緑内障の新しい代替診断法となると考えられる。
[/su_tab][/su_tabs]
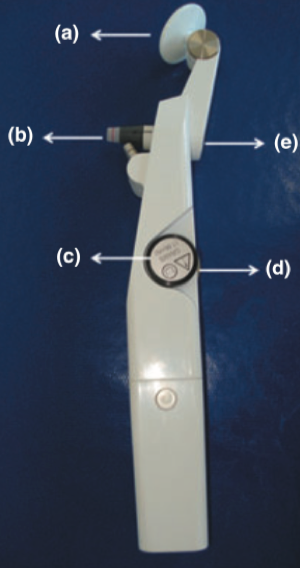
Perkin圧平式眼圧計(Figure 1より引用)
