犬の角膜内皮細胞ジストロフィーの治療としての表層角膜切除術後の角膜コラーゲン・クロスリンキング: 予備臨床研究
Corneal collagen cross-linking following superficial keratectomy as treatment for corneal endothelial cell dystrophy in dogs
犬の角膜内皮細胞ジストロフィーの治療としての表層角膜切除術後の角膜コラーゲン・クロスリンキング: 予備臨床研究
Kim J, Ji D-B, Takiyama N, Bae J, Kim M-S. Corneal collagen cross-linking following superficial keratectomy as treatment for corneal endothelial cell dystrophy in dogs: Preliminary clinical study. Vet Ophthalmol 2018;57(15):690. / PMID: 30109755
論文アブストラクト(PubMed)はこちら
To describe the outcome of corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL) combined with superficial keratectomy (SK) as treatment for corneal edema due to corneal endothelial dystrophy (CED) in dogs.
ANIMALS STUDIED:
Four eyes of four dogs (3 Shih Tzus and 1 English Cocker Spaniel) with corneal edema due to CED were treated with SK and CXL. Two were males, and two were females.
PROCEDURE:
Depending on corneal thickness, 500-700 μm of edematous cornea was removed by SK. Next, CXL was performed by irradiating the cornea with UVA (365 nm) at 3 mW/cm² irradiance for 30 min after soaking with 0.1% riboflavin in 20% dextran every three minutes for 30 minutes. One drop of riboflavin was instilled every three minutes during irradiation. Slit lamp biomicroscopy and optical coherence tomography were used to examine the cornea during the follow-up period.
RESULTS:
The corneas had focal to diffuse edema, and the average corneal thickness was 1553 (1282-1900) μm. All corneas showed a significantly reduced corneal thickness and regained marked transparency immediately after treatment; however, the opacity increased as the corneal thickness increased during the follow-up period. Corneal vascularization (n = 4) disappeared within a month. Corneal pigmentation (n = 1) and bullae (n = 1) were observed. All cases showed marked reduction in corneal thickness; however, transparency was improved in only one case.
CONCLUSION:
Collagen cross-linking with SK has the potential to reduce the corneal thickness in CED cases; however, a lasting clinically significant improvement of corneal transparency seems unlikely. As the added benefit of CXL to the SK procedure is unclear based on the results of this study, combined treatment of CXL and SK for the treatment of corneal edema caused by CED is currently not recommended in dogs.
KEYWORDS:
corneal collagen cross-linking; corneal endothelial dystrophy; dog; superficial keratectomy
犬の角膜内皮ジストロフィー(CED:corneal endothelial dystrophy)による角膜浮腫の治療としての表層角膜切除術(SK:superficial keratectomy)と組み合わせた角膜コラーゲンクロスリンキング(CXL:corneal collagen cross-linking)の結果を報告すること。
研究動物:
CEDによる角膜浮腫を有する4頭の犬(3頭のシーズーおよび1頭のイングリッシュコッカースパニエル)の4眼をSKおよびCXLで治療した。 2頭は雄、2頭は雌でした。
手順:
角膜の厚さに応じて、500〜700μmの浮腫性角膜をSKによって除去した。次に、0.1%リボフラビン (20%デキストラン)中に浸漬した後、3分間毎に3mW /cm2の照度で30分間UVA(365nm)を角膜に照射することによりCXLを行った。照射中、3分毎にリボフラビンを一滴滴下した。フォローアップ期間中、スリットランプ生体顕微鏡検査および光干渉断層撮影を使用して角膜を検査した。
結果:
角膜は限局性〜びまん性の浮腫があり、平均角膜厚は1553(1282-1900)μmであった。処置後直ちに、全ての角膜で、角膜厚が有意に減少し、透明性は顕著に回復した。しかしながら、追跡期間中に角膜の厚さが増すにつれて不透明度は増加した。角膜血管新生(n=4)は1ヶ月以内に消失した。角膜色素沈着(n=1)および水疱(n=1)が観察された。全ての症例が角膜厚の著しい減少を示した。しかし、透明度が改善されたのは1症例のみであった。
結論:
コラーゲンクロスリンキングを組み合わせた表層角膜切除術は、CEDの症例に対して角膜厚を減少させる可能性がある。しかしながら、角膜の透明度における、持続的で臨床的に重要な改善は認められない可能性が高い。この研究の結果に基づくと、SK処置に対する、CXLのさらなる利点は不明であるので、犬のCEDによって引き起こされる角膜浮腫の治療のためのCXLとSKの併用治療は、現段階では推奨されない。
キーワード:
角膜コラーゲンクロスリンキング、角膜内皮ジストロフィー、犬、表層角膜切除
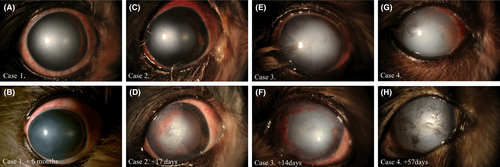
表層角膜切除術と角膜クロスリンキングを併用した犬の症例の術前・術後の前眼部写真 (Fig2より引用)
