難治性緑内障に対してマイクロパルス経強膜光凝固術により治療した犬30頭の予備所見結果
Preliminary findings in 30 dogs treated with micropulse transscleral cyclophotocoagulation for refractory glaucoma.
難治性緑内障に対してマイクロパルス経強膜光凝固術により治療した犬30頭の予備所見結果
Sapienza JS, Kim K, Rodriguez E, DiGirolamo N. Preliminary findings in 30 dogs treated with micropulse transscleral cyclophotocoagulation for refractory glaucoma. Vet Ophthalmol. 2018;45:1283. doi:10.1111/vop.12622. / PMID: 30358935
論文アブストラクト(PubMed)はこちら
OBJECTIVE:
The purpose of this study was to report the preliminary results of a novel micropulse transscleral diode laser cyclophotocoagulation (MP-TSCP) as primary therapy for glaucomatous dogs.
ANIMAL STUDIED:
Client owned dogs undergoing MP-TSCP therapy at a veterinary referral center.
PROCEDURE:
Retrospective study of dogs with glaucoma that were treated with MP-TSCP with a minimum of 1 month (range: 1-18 months) of follow-up. Reported outcomes were intraocular pressure (IOP), treatment parameters, reduction in medications, complications, and incidence of repeat therapy.
RESULTS:
Thirty dogs (35 eyes) were evaluated. The mean age was 9.0 years. Mean preoperative IOP was 34.5 mm Hg. Mean postoperative IOP at 1 month (35/35 eyes) was 22 mm Hg, 2 months (26/35 eyes) was 20.5 mm Hg, 4 months (20/35 eyes) was 19 mm Hg, 6 months (10/35 eyes) was 19 mm Hg, 12 months (8/35 eyes) was 21 mm Hg. First treatment success rate was 19/35 eyes (54.3%). Repeat laser was performed in 11 eyes with 4/11 eyes responding favorably for a total IOP control of 23/35 eyes (65.7%). Mean energy levels employed were 137.5 seconds and 2351 mW at 31.3% duty cycle. Reduction in medications was from a mean of 3.6 medications preoperatively to 3.1 medications postoperatively. Complications included corneal ulcers 5/35 eyes (14.3%), uncontrolled IOP in 12/35 eyes (34.3%) and repeat treatment in 11/35 eyes (31.4%).
CONCLUSIONS:
MP-TSCP was successful in controlling IOP in most patients as well as to reduce postoperative medications with minimal resultant intraocular inflammation and complications. The micropulse procedure also can be repeated. Future investigations to study effective treatment parameters are warranted in a larger series of patients over a longer period of evaluation.
目的:
本研究の目的は、緑内障犬の治療として、新しいマイクロパルス経強膜ダイオードレーザー光凝固術(MP-TSCP)の予備結果を報告することであった。
動物:
二次診療施設でMP-TSCPによる治療を受けた飼育犬。
手順:
緑内障の犬をMP-TSCPで処置した犬の回顧的調査で、最低1ヶ月(範囲:1〜18ヶ月)の追跡調査を行った。調査したアウトカムは、眼圧(IOP)、治療パラメータ、投薬量の減少、合併症、および反復治療率であった。
結果:
30頭の犬(35眼)を評価した。平均年齢は9.0歳であった。平均術前IOPは34.5mmHgであった。 1ヵ月(35/35眼)の平均術後IOPは22 mmHg、2ヵ月(26/35眼)は20.5 mmHg、4ヵ月(20/35ヵ月)は19 mmHg、6ヵ月(10/35眼)は19mmHg、12ヶ月(8/35眼)は21mmHgであった。最初の治療成功率は19/35眼(54.3%)であった。再度のレーザー処置は11眼で実施され、4/11眼は23/35眼(65.7%)の全IOPコントロールに対して良好に応答した。使用された平均エネルギーレベルは、31.3%のデューティサイクルで137.5秒および2351mWであった。投薬量の減少は、術前の平均3.6投薬から術後3.1投薬であった。合併症には、角膜潰瘍5/35眼(14.3%)、12/35眼(34.3%)においてIOPコントロールの失敗、11/35眼(31.4%)における反復治療が含まれた。
結論:
MP-TSCPは、ほとんどの患者において眼圧を制御することに成功し、眼内炎症および合併症を最小限に抑えて術後薬剤を減少させた。マイクロパルスの手技は繰り返すことができる。効果的な治療パラメータを評価するためには、長期の評価期間を伴うより大規模な研究が必要である。
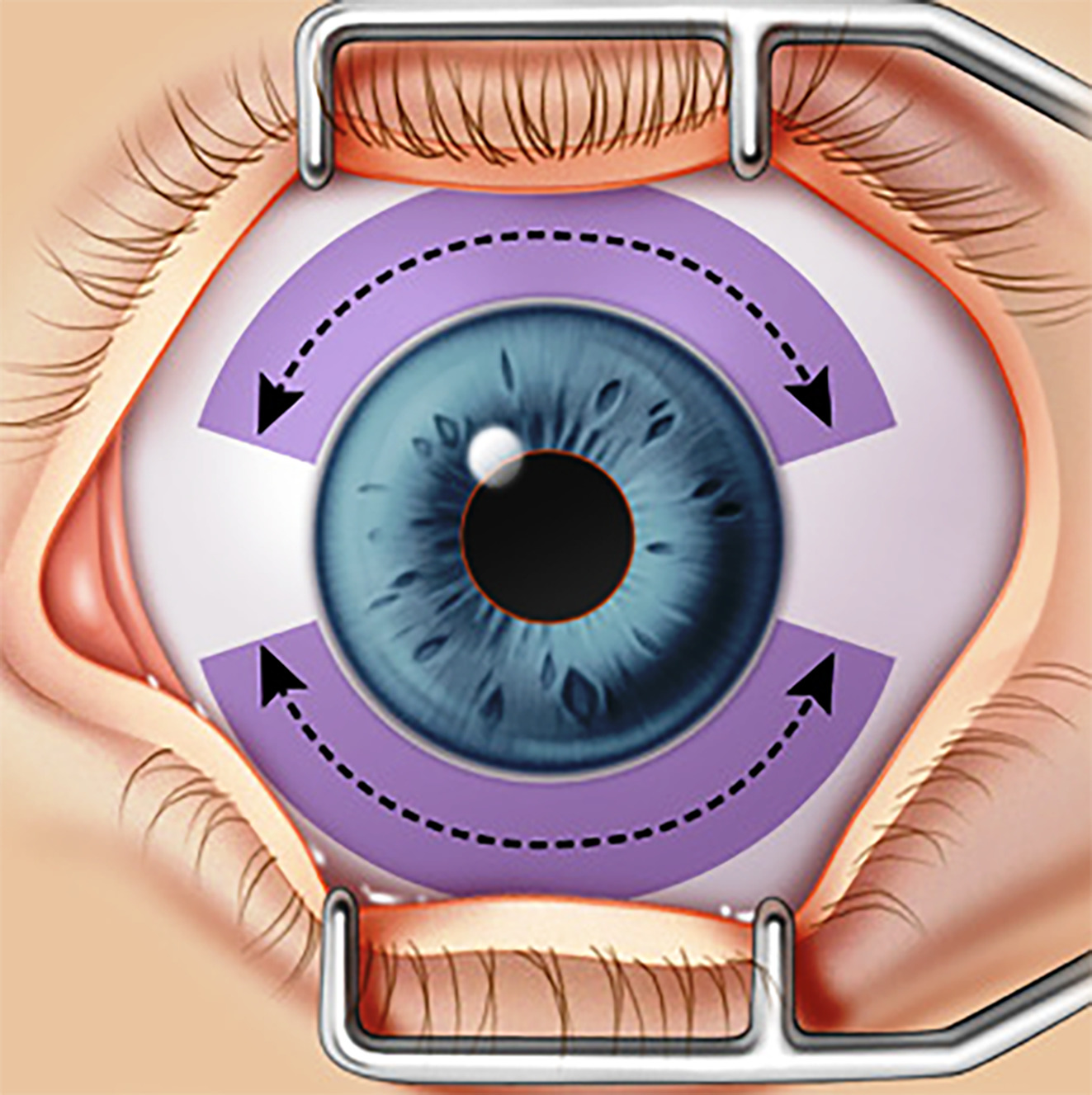
(3時と9時方向を避けて、腹側および背側にマイクロパルスプローブを照射。図1より引用。
コメント書く
