イヌの眼用10%フェニレフリン点眼の心血管効果
Cardiovascular effects of topical ophthalmic 10% phenylephrine in dogs
イヌの眼用10%フェニレフリン点眼の心血管効果
Herring IP, Jacobson JD, Pickett JP. Cardiovascular effects of topical ophthalmic 10% phenylephrine in dogs. Vet Ophthalmol. 2004;7(1):41-46. / PMID: 14738506
論文アブストラクト(PubMed)はこちら
To evaluate the effect of topical ophthalmic 10% phenylephrine on systolic arterial pressure (SAP), diastolic arterial pressure (DAP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), pulse rate (PR) and electrocardiogram (ECG) in dogs.
ANIMALS STUDIED:
Nine clinically normal dogs.
PROCEDURE:
Arterial catheters were placed in the dorsal pedal artery of awake dogs and ECG leads were attached. After a 15-min acclimatization period, baseline PR, SAP, DAP and MAP were recorded every 5 min for 20 min. Two treatment groups (eight dogs each) were studied. Group I: one drop of phenylephrine was placed in each eye once. Group II: one drop of phenylephrine was placed in each eye three times at 5-min intervals. Following treatment, PR, SAP, DAP and MAP were recorded every 5 min for 90 min. The mixed procedure of the SAS system was used to perform a repeated measures analysis of variance to test for linear and quadratic trends across time.
RESULTS:
Group I: There was a significant quadratic decrease in PR across time (P = 0.0051). Systolic arterial pressure increased linearly with time (P = 0.0002), MAP increased linearly with time (P = 0.0131), and DAP increased linearly with time (P = 0.0001). Group II: There was a significant quadratic decrease in PR across time (P = 0.0023). There was a significant quadratic increase in SAP (P = 0.0324), MAP (P = 0.0103) and DAP (P = 0.0131) across time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Topical ophthalmic application of 10% phenylephrine in normal dogs results in elevation of arterial blood pressure and reflex bradycardia.
局所10%フェニレフリン点眼薬の収縮期動脈圧(SAP),拡張期動脈圧(DAP),平均動脈圧(MAP),脈拍数(PR)と心電図(ECG)に対する影響をイヌで評価した。
研究動物:
臨床上正常な9頭のイヌ
方法:
覚醒しているイヌの足背動脈に動脈カテーテルを設置し、ECGの導線を装着した。15分間の馴化期間の後、ベースラインPR、SAP、DAPおよびMAPを5分ごとに20分間記録した。2つの治療群(8頭ずつ)で研究された。1群:各眼に1回フェニレフリンを1滴入れた。2群:各眼に5分間隔で3回フェニレフリンを1滴入れた。投与後、PR、SAP、DAP、MAPを5分毎に90分間記録した。統計プログラムSASシステムを用いて,経時的に線形および二次的傾向をテストするために,繰り返しANOVAを実施した。
結果:
1群:PRは時間に対し、有意な二次曲線的低下を示した(P=0.0051)。SAP(P=0.0002)、MAP(P=0.0131)、DAP(P=0.0001)は時間に対し直線的に上昇した。2群:PRは時間に対し、有意な二次曲線的低下を示した(P=0.0023)。SAP(P = 0.0324),MAP(P = 0.0103),DAP(P = 0.0131)では時間の経過とともに有意な二次的増加が認められた。
結論:
正常犬への10%フェニレフリン点眼投与は、動脈血圧の上昇や反射性徐脈を起こす。
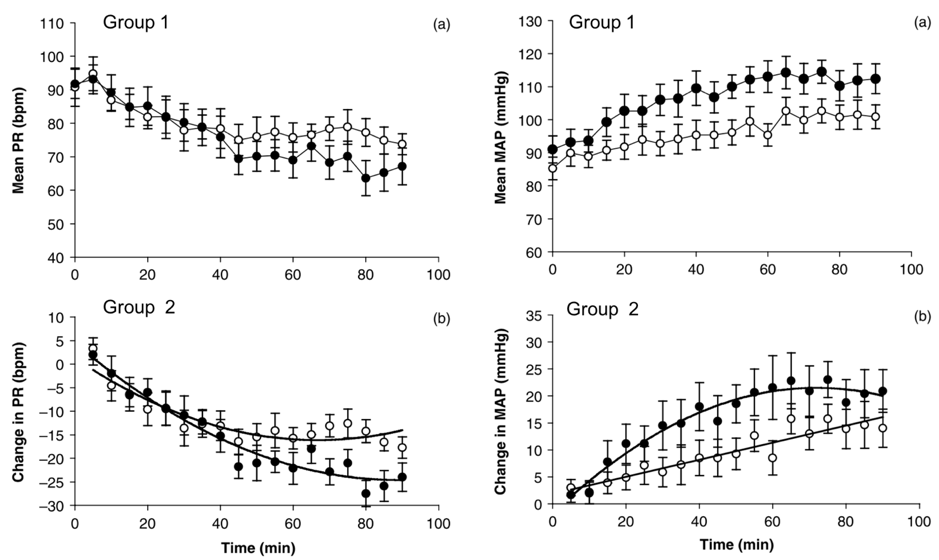
(左図)グループ1および2のイヌの10%フェニレフリン点眼に対する脈拍数の経時的変化
(右図)グループ1および2のイヌの10%フェニレフリン点眼に対するMAPの経時的変化
